Near-infrared (NIR) dyes are the category of molecules that absorb light in the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (typically 700-900 nm) and emit light at a slightly longer wavelength. Upon absorption of light at a specific wavelength, these molecules briefly enter an excited state and then return to their ground state by emitting light at a lower energy (longer wavelength, emission). This distinctive characteristic enables them to “glow” when exposed to NIR light, making them useful for imaging.
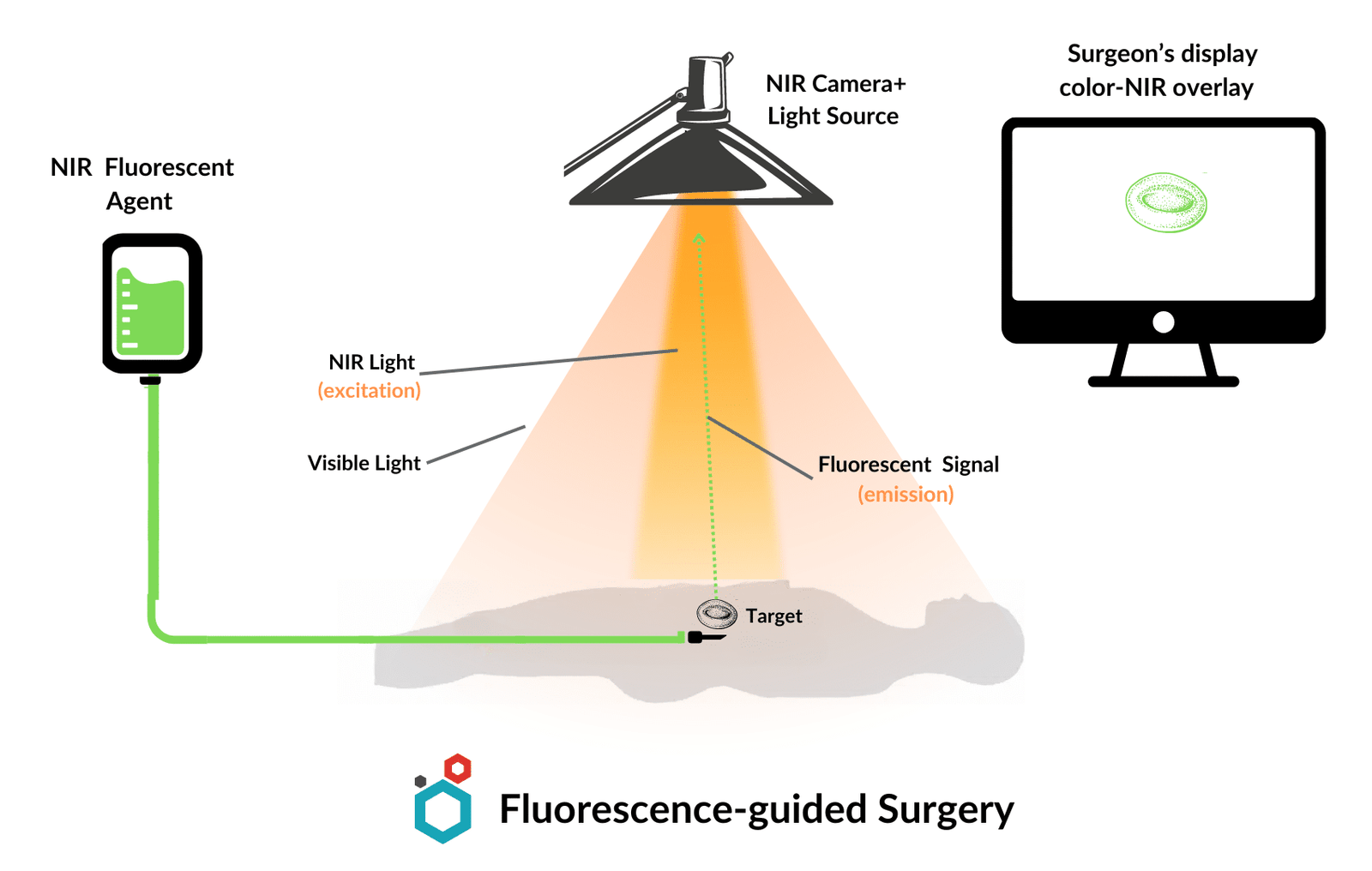
NIR light can penetrate deeper into tissues compared to visible light, enabling visualization of structures and processes within living organisms. Also, biological tissues produce less background fluorescence in the NIR range, resulting in clearer images with higher contrast. NIR dyes can thus serve as valuable tools for in-vivo imaging offering advantages such as – being non-invasive, allowing dynamic monitoring of biological processes, targeted imaging as NIR dyes can be conjugated to specific molecules, like antibodies, to highlight particular cells or tissues of interest.
Macsen offers custom synthesis services of NIR dyes including development of molecule, process optimization and scaling up of developed process. For enquiries, reach out to us at sales@macsenlab.com.
Table of Contents
Classification of NIR dyes
Based on Chemical Structure
Cyanine Dyes
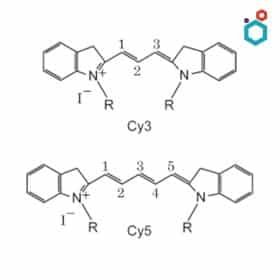
- Structure: These dyes are characterized by a polymethine chain that connects two heterocyclic nitrogen-containing rings.
- Properties: Cyanine dyes offer bright fluorescence, tunable emission wavelengths, and good photostability.
- Examples: Indocyanine Green (ICG), IRDye 800CW
- Applications: Angiography (blood vessel imaging), tumor imaging, and lymphatic mapping.
Squaraine Dyes
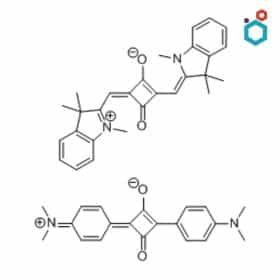
- Structure: Squaraine dyes contain a central squarylium ring with electron-donating groups attached.
- Properties: These dyes are known for their intense absorption and emission in the NIR region, as well as their high quantum yield.
- Examples: IRDye 800RS, SQ-212
- Applications: Tumor imaging, cell tracking, and diagnostics
Porphyrin-Based Dyes
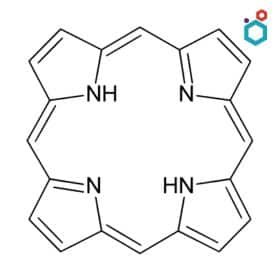
- Structure: These dyes are based on the porphyrin ring system, which is also found in hemoglobin and chlorophyll.
- Properties: They exhibit strong absorbance in the visible and NIR range, making them versatile for various imaging modalities.
- Examples: Protoporphyrin IX (PpIX), Chlorin e6
- Applications: Tumor imaging, photodynamic therapy, and angiography.
Other Dyes
- Xanthene Dyes
- D-A-D Dyes
- BODIPY Dyes
- Fluorescent Proteins
- Quantum Dots
Based on Wavelength
NIR-I dyes
These dyes absorb and emit light in the shorter near-infrared region, typically between 700-900 nm. While they provide acceptable resolution for imaging, their penetration depth in tissues is restricted, due to greater light scattering at these wavelengths. Examples include Indocyanine Green (ICG), IRDye 800CW, etc.
NIR-II dyes
NIR-II dyes absorb and emit light in the longer near-infrared region, ranging from 900-1700 nm. Because there is less dispersion at longer wavelengths, deeper tissue penetration is possible. Examples include CH1055-PEG (a modified cyanine dye), IR-1061, and other experimental dyes.
| Feature | NIR-I dyes (700-900 nm) | NIR-II dyes (1000-1700 nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Penetration | Moderate | Deep |
| Resolution | Good | Excellent |
| Autofluorescence | Low | Very Low |
Applications of NIR Dyes in-vivo Imaging
NIR Dyes have paved the way for a range of possibilities for visualizing and understanding biological processes within living organisms. Some of the common in-vivo applications where NIR dyes are used, are as follows –
Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping (SLNM)
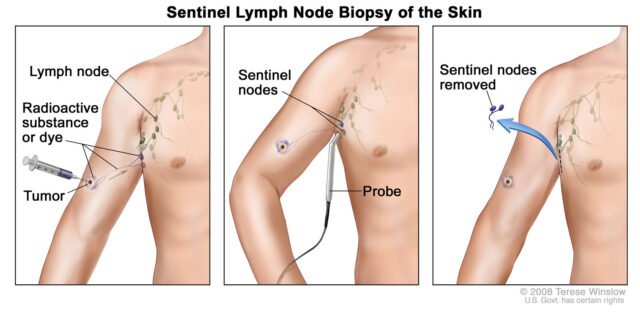
The sentinel lymph nodes are the first lymph nodes to which cancer cells may spread from the original tumor. Sentinel lymph node mapping is a medical procedure used to identify if cancer has spread from the primary tumor to the lymphatic system.
How NIR Dyes Help? A NIR dye, such as indocyanine green (ICG), is injected near the tumor site. It travels through lymphatic vessels and accumulates in the sentinel lymph nodes. Surgeons can then easily identify and remove these nodes for biopsy, aiding in cancer staging and treatment planning.
| Dye | Clinical Trial |
|---|---|
| Indocyanine Green | FDA approved, Widely used |
| SGM-101 | Phase II Trials |
Tumor Margin Visualization & Surgery
NIR dyes that preferentially bind to tumor cells can be used to “light up” the tumor, directing surgeons to its exact position and size. Those with a high affinity for specific tumor markers (e.g., EGFR, HER2) can clearly delineate the boundary between the tumor and healthy tissue. This real-time imaging enhances tumor removal accuracy and achieves precise resections while potentially lowering the chance of recurrence.
| Dye | Clinical Trial |
|---|---|
| OTL38 (Pafalocianine) | FDA approved |
| LS301 | Phase I/II Trials |
| CLR1502 | Phase I/II Trials |
| BLZ-100 | Early Phase |
| MM-302 | Phase-I |
Angiogenesis Imaging
Angiogenesis imaging focuses on observing the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), which aids tumor growth and spread. NIR dyes that bind to angiogenesis markers (such as VEGF) enable non-invasive monitoring of tumor vascularity. This data can be used to track therapy progress and forecast outcomes.
The NIR dye HX005, is currently in preclinical studies with potential for trials.
Lymphatic Imaging
Lymphatic imaging involves assessing the structure and function of the lymphatic system, which plays a crucial role in immune function and cancer metastasis. NIR dyes can help visualize lymphatic vessels and track the flow of lymph, aiding in the diagnosis of lymphatic disorders and assessing the risk of cancer spread.
| Dye | Clinical Trial |
|---|---|
| BLZ-150 | Early Stage |
| OTL703 | Preclinical/Early trials, focus on breast cancer |
Other Applications
NIR dyes are also being investigated for:
- Image-Guided Drug Delivery: NIR dyes attached to therapeutic agents allow for targeted delivery and monitoring of drug distribution within tumors.
- Inflammation Imaging: NIR dyes that bind to inflammatory markers can help visualize and monitor inflammatory conditions.
- Cardiac Imaging: NIR dyes can assess blood flow and perfusion in the heart, aiding in the diagnosis of heart diseases.
FDA Approved NIR Dyes
Indocyanine Green (ICG)
Indocyanine Green is a cyanine dye with peak absorption and emission in the NIR-I range, offering moderate tissue penetration. It stands as the most widely used and versatile NIR dye in clinical practice.
Applications:
- Angiography: Visualizing blood vessels to assess circulation and detect abnormalities.
- Tumor Surgery: Identifying tumor margins and guiding surgical resection.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping (SLNM): Determining the spread of cancer cells in lymphatic systems.
- Other: Used in ophthalmic angiography, liver function assessment, and more.
Strengths:
- Well-established safety profile
- Relatively inexpensive
- Versatile for multiple applications
Limitations:
- Limited tissue penetration compared to NIR-II dyes
- Non-specific binding, requiring conjugation for targeted imaging
Methylene Blue
Methylene Blue is a multifaceted blue colored dye which exhibits some fluorescence in the NIR-I region.
Applications:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Used to stain lymph nodes for easier identification during surgery.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): When activated by light, it can generate reactive oxygen species to destroy cancer cells.
OTL38 (Pafolacianine)
Pafolacianine is a folate-targeted NIR fluorescent imaging agent. It binds to folate receptors, often overexpressed in ovarian cancer cells, allowing surgeons to visualize cancerous tissue.
Applications:
- Ovarian Cancer Surgery: Aids in the intraoperative identification of malignant ovarian cancer lesions.
Strengths:
- Targeted approach enhances specificity
- Real-time visualization during surgery
Limitations:
- Currently approved only for ovarian cancer
- Requires a specific NIR fluorescence imaging system
Promising NIR Dyes in Clinical Trials
NIR-I Dyes
- Bevacizumab-IRDye800CW: This targeted imaging agent combines the anti-angiogenic drug bevacizumab with the NIR dye IRDye800CW. This conjugate aims to visualize and monitor tumors more effectively during surgery and potentially improve treatment response assessment. It is currently in Phase I/II Trials.
- SGM-101: Currently in Phase II trials, this cyanine-like dye is being investigated for sentinel lymph node mapping, a critical step in cancer staging.
NIR-II Dyes
- CH1055-PEG: This modified cyanine dye is one of the first NIR-II dyes to be tested in humans. It has shown promising applications in tumor visualization and deep tissue imaging, offering advantages over traditional NIR-I dyes. It is currently in Phase II trials.
For a complete list of NIR dyes with their potential applications and trial phase, please click here.
Resources on Indocyanine Green –
Indocyanine Green | Chemical Properties, Uses and Side Effects
Indocyanine Green Injection for Angiography
Indocyanine Green | Uses in Medical Imaging & Surgery
Resources on Methylene Blue –
Methylene Blue | Chemistry, Uses & Side effects
Methylene blue for treating Methemoglobinemia
Methylene Blue & Covid-19 – Research So Far
Staining with Methylene Blue | Different uses and examples
Methylene Blue’s uses in Fish Aquaculture
Methylene Blue Against Cyanide Poisoning
Methylene Blue Injection: Indications, Dosage & Brands
Methylene Blue in the treatment of Alzheimer’s
Malaria Treatment with Methylene Blue
Methylene Blue treatment for Lumpy Skin disease in cattle

