Indocyanine green (ICG) or Indocarbocyanine is a nontoxic, tricarbocyanine water-soluble dye known for its fluorescent properties when exposed to near-infrared light. It has emerged as a revolutionary tool in the field of medical diagnostics and therapeutic procedures, offering unparalleled insights and advantages in both medical imaging and surgery.
Table of Contents
ICG in Medical Imaging
Indocyanine Green is extremely useful in medical imaging, particularly because of its properties that allow for the visualization of vascular structures and organ perfusion through near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence. This capability makes it valuable in a range of diagnostic and surgical applications. Following are the applications of ICG in medical imaging across various medical fields:
Cardiac and Vascular Imaging
While not traditionally associated with mainstream cardiac imaging techniques such as echocardiography, MRI, or CT scans, ICG provides unique advantages in specific contexts, particularly in the visualization of blood flow and vascular structures.
ICG is used to measure cardiac output through a method known as ICG pulse dye densitometry. After intravenous administration, the dye’s concentration is monitored as it circulates through the heart, allowing for the calculation of cardiac output based on the dilution principle. This method is less commonly used today, with other techniques like thermodilution and echocardiography being more prevalent for cardiac output measurement. However, it offers a non-invasive alternative in certain clinical or research settings.
During coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, ICG fluorescence angiography can be employed to assess the patency of coronary artery bypass grafts. After the grafts are placed, ICG is administered, and a specialized NIR camera is used to visualize the flow of ICG through the grafts, confirming their patency and ensuring proper blood flow to the heart muscle.
Ophthalmology
Indocyanine Green (ICG) plays a crucial role in ophthalmology, primarily through its use in ICG angiography, a diagnostic procedure that helps visualize the blood vessels in the eye, especially those of the choroid—the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera and retina. This imaging technique is useful for diagnosing and monitoring conditions like age-related macular degeneration, central serous chorioretinopathy, and other retinal diseases. The ability of ICG to provide high-contrast images helps in identifying neovascularization and other pathologies that may not be visible with traditional imaging techniques.
Indocyanine Green Angiography
Indocyanine green angiography or ICGA is a diagnostic procedure that uses ICG pigment to study blood flow in the choroid (the layer of blood vessels beneath the retina). Indocyanine green dye is injected into the veins of the arm/hand. ICG can bind 98% to plasma proteins (80% to globulin, 20% to alpha lipoproteins and albumin), resulting in less leakage (dye leakage from blood vessels) compared to fluorescein as a marker.
Pictures are taken to record the blood flow as the dye flows through the blood vessels of the eye. Choroidal blood vessels are hidden under a layer of pigmented cells. The infrared light emitted by the ICG dye can be imaged through a tinted layer using a special filter. The most common use of indocyanine green angiography is the detection of choroidal neovascularization, a common component of age-related macular degeneration.

Lymphatic Mapping
Indocyanine Green (ICG) is highly valuable in the field of lymphatic mapping due to its fluorescent properties when exposed to near-infrared (NIR) light. It aids in the visualization of lymphatic vessels and nodes. Lymphatic mapping with ICG is particularly crucial in surgeries for cancers, such as breast cancer or melanoma, where procedures such as lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node (the first node to which cancer cells are likely to spread from a primary tumor) biopsy (SLNB) are essential for staging and treatment planning.
Indocyanine Green Lymphography
Indocyanine green lymphography or Indocyanine green lymphangiography is an emerging imaging technique used to visualize lymphatic vessels and map their course as they drain to sentinel lymph nodes. ICG, when injected into the interstitial fluid, is taken up by lymphatic vessels and transported to regional lymph nodes. Using NIR fluorescence imaging equipment, clinicians can visualize this movement in real time. The real-time images show the flow of lymph and help in identifying blockages, leaks, or other abnormalities in the lymphatic system.
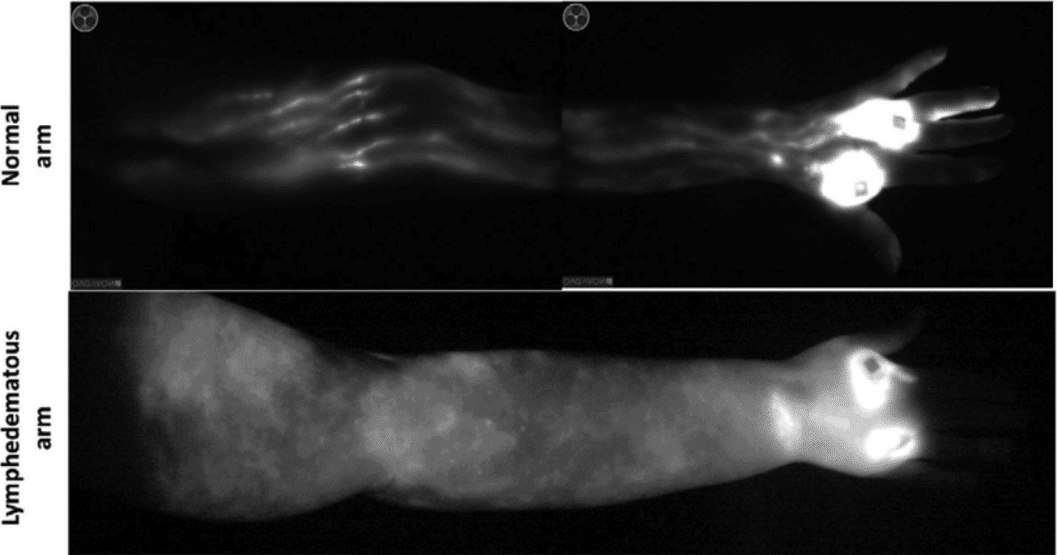
ICG lymphography was initially used for breast sentinel node biopsy. Its application then extended to lymphoedema diagnosis and mapping of lymphatic vessels before lymphovenous anastomosis (LVA) surgery. Gastric cancer lymphatic drainage can also be visualized using indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence lymphography.
Liver Function Tests
ICG clearance is a useful diagnostic test to evaluate liver function and hepatic blood flow. Since ICG is exclusively eliminated by the liver, its rate of clearance can indicate the functional capacity of the liver. It does not undergo any metabolism in the liver, making it an excellent marker for assessing liver function. This test is particularly important for the assessment of hepatic function, identifying liver diseases, evaluation before hepatic surgery, and monitoring of liver health.
ICG in Surgery
Indocyanine Green is a fluorescent dye that, when used in various surgical procedures, provides real-time visualization of vascular flow, tissue perfusion, and critical anatomical structures. This capability enhances surgical precision and safety across multiple disciplines. Some key applications of ICG in surgical procedures are:
In Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, commonly referred to as a lap chole, is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the gallbladder. It is typically performed to treat gallstones and their complications, such as inflammation, infection, or pain associated with gallstones (cholecystitis). Laparoscopic cholecystectomy requires precise identification of the cystic duct, common bile duct, and artery to prevent injuries and ensure the safety and effectiveness of the surgery.
The primary advantage of using ICG in laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the enhanced visualization of the biliary tree. It allows surgeons to see the biliary structures in real-time during the surgery, aiding in the identification of the cystic duct, common bile duct, and cystic artery with greater clarity. The enhanced visualization provided by ICG fluorescence imaging also significantly reduces the risk of bile duct injuries, especially beneficial in complicated cases, such as those with acute cholecystitis, severe inflammation, or anomalous biliary anatomy.
In Colorectal Surgery
Colorectal surgery refers to a range of surgical procedures performed on the colon, rectum, and anus to treat diseases and conditions affecting these parts of the body. This type of surgery is commonly used to manage colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, and other conditions such as rectal prolapse and severe constipation.
ICG has emerged as a valuable tool in colorectal surgery, enhancing surgical outcomes through improved visualization of blood flow, tissue perfusion, and lymphatic mapping. ICG fluorescence angiography is used intraoperatively to assess the perfusion of the bowel segments involved in the anastomosis. After intravenous injection, ICG binds to plasma proteins and remains within the vasculature, allowing surgeons to visualize blood flow in real-time using near-infrared (NIR) imaging.
Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy, facilitated by ICG, improve the accuracy of staging and treatment plans in colorectal cancer surgery.
In Oral Cancer Surgery
Recent studies have explored the efficacy and safety of ICG in oral cancer management, with many highlighting its potential to improve surgical accuracy and patient outcomes. Its ability to enhance the visualization of cancerous tissues and lymphatic pathways offers a significant advantage in the precise and effective treatment of oral cancer.
ICG fluorescence imaging aids surgeons in real-time visualization of tumor margins, ensuring more precise removal of malignant tissues while sparing as much healthy tissue as possible. Also, oral cancer often spreads through the lymphatic system. Thus, ICG can be used to perform lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy, aiding in the accurate staging of cancer and planning of treatment.
In Reconstructive Surgery
Indocyanine Green fluorescence imaging is increasingly used in reconstructive surgery to enhance the success rate of procedures by providing real-time visualization of blood flow and tissue perfusion. This application is critical as adequate vascularization is essential for the survival of flaps and grafts used in reconstructive procedures. The ability to continuously monitor perfusion during surgery without additional invasive procedures is a significant advantage. This technology enhances the precision of surgical outcomes, reduces the risk of complications, and ultimately contributes to improved patient recovery and satisfaction.
Upcoming Advancements
The integration of ICG with cutting-edge imaging technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and robotic-assisted surgery, represents the forefront of surgical innovation. Also, the development of more sensitive cameras and visualization systems capable of detecting ICG fluorescence at lower concentrations and deeper tissue levels is expected. These advancements in imaging technology and surgical instruments will enable surgeons to visualize anatomical structures with unprecedented clarity and precision, enhancing the effectiveness and safety of surgical procedures.
Moreover, ongoing research into ICG’s pharmacokinetics and its interactions with various tissues is paving the way for new applications, including targeted drug delivery and photodynamic therapy.
Resources on Indocyanine Green
Indocyanine Green | Chemical Properties, Uses and Side Effects
Indocyanine Green Injection for Angiography
Disclaimer-
The information provided here is based on general knowledge, articles, research publications etc and we do not claim the authenticity of any of the information provided above. We do not claim or suggest/advise any medical, therapeutic, health or nutritional benefits of Indocyanine green. We do not supply or promote our Indocyanine green product for the applications which are covered by valid patents and which are not approved by the FDA.
Macsen Labs is a manufacturer and supplier of high-quality Indocyanine Green.

