Home »Sourcing Solutions » Prilocaine
What is Prilocaine
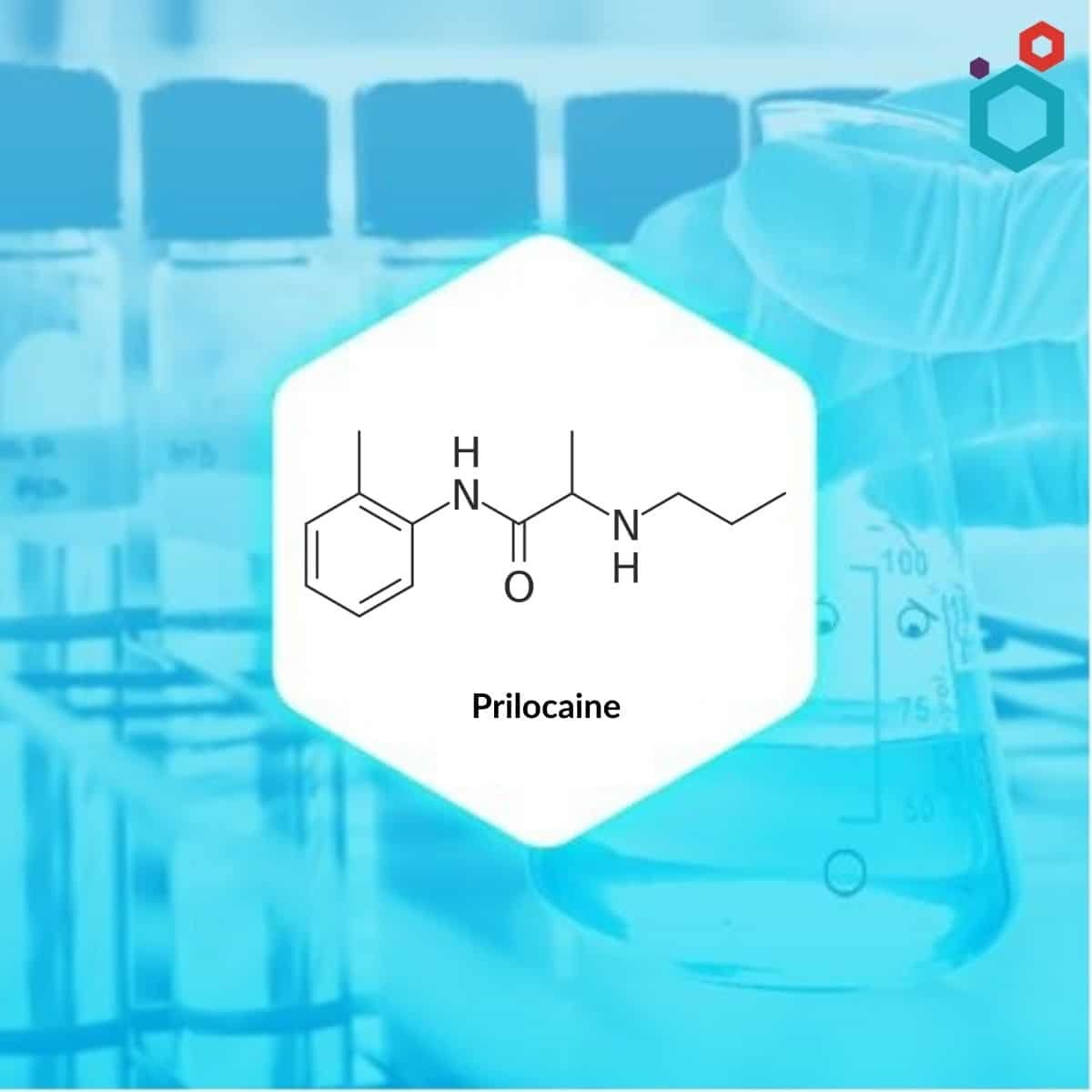
Prilocaine is a toluidine derivative and is a secondary amide analogue of lidocaine. It is used as a general local anaesthetic drug for pain relief with a prolonged duration of action and rapid onset than other similar medicines.
| PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| Name of Product | Prilocaine |
| IUPAC Name | N-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(propylamino)propanamide |
| Synonyms | Propitocaine; Citanest; Prilocainum; prilocaine base; N-(2-Methylphenyl)-2-(propylamino)propanamide; Astra 1515; o-Methyl-2-propylaminopropionanilide; Prilocaina |
| CAS No | 721-50-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H20N2O |
| Molar Mass | 220.31 g/mol |
| Pubchem CID | 4906 |
| Pubchem SID | 469688496 |
Chemical Properties
| SR. No | Criteria | Limit/Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Appearance (Form) | Solid |
| 2 | Appearance (Colour) | White |
| 3 | Odour | Odourless |
| 4 | Taste | Initially acid & then bitter taste |
| 5 | Melting point | 37-38 °C |
| 6 | Solubility | Freely soluble in alcohol Slightly soluble in Chloroform Practically insoluble in Ether |
| 7 | Stability/Shelf life | Stable in Light & Air |
Mechanism of action
By preferentially binding to and preventing depolarization of the voltage-gated sodium channel, prilocaine stabilises the neuronal membrane. As a result, the membrane’s permeability is reduced, which in turn inhibits the ionic sodium inflow necessary for impulse initiation and conduction.
Uses
- Currently, it is used most often for infiltration anaesthesia in dentistry.
- It is also used as a topical preparation (in combination with lidocaine) for dermal anaesthesia for the treatment of conditions like paresthesia.
However, the use of prilocaine is contraindicated in people with sickle cell anaemia, anaemia, or symptomatic hypoxia.
Side effects
Common side effects of lidocaine include:
- Mild burning where the medicine is applied
- Itching, rash
- Changes in skin colour where the medicine was applied
Serious side effects of lidocaine include:
- Severe burning, stinging, or irritation at the application site
- Swelling or redness
- Sudden dizziness or drowsiness after medicine is applied
- Confusion, blurred vision, ringing in your ears
- Bruising or purple appearance of the skin
- Unusual sensations of temperature
Prilocaine causes less neurological and cardiac toxicity than other amide local anaesthetics but is associated with the potential of causing methemoglobinemia.
FAQs
Q. What is lidocaine and prilocaine cream used for?
Lidocaine and prilocaine topical cream is used on the skin or in the genital area to cause numbness or loss of feeling before certain medical procedures. It is also used to prevent pain caused by an injection, the drawing of blood from a vein, or minor surgeries such as removing warts.
Q. What is the difference between prilocaine and lidocaine?
Prilocaine is an analogue of lidocaine that is a secondary amide, and it has a longer duration of action in addition to a rapid onset.
Q. Is prilocaine the same as novocaine?
The name “novocaine” is often used to denote several forms of local anaesthetic, such as Xylocaine (lidocaine ), Citanest (prilocaine ), or Septocaine (articaine ).
Buy the best quality Prilocaine through Macsen Laboratories.
