Home » Speciality Dyes and Biological Stains » Rhodamine B
What is Rhodamine B?
Rhodamine B is a type of amphoteric dye that is frequently employed as a fluorochrome. It is an organic chloride salt and a xanthene dye. As the temperature rises, there is a corresponding drop in the fluorescence intensity of rhodamine B.
Rhodamine B is capable of coexisting in equilibrium as both its “open” or fluorescent form and its “closed” or nonfluorescent spirolactone form. When exposed to an acidic environment, the “open” form predominates, whereas the “closed” form is colorless and predominates when exposed to a basic environment.
| PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| Name of Product | Rhodamine B |
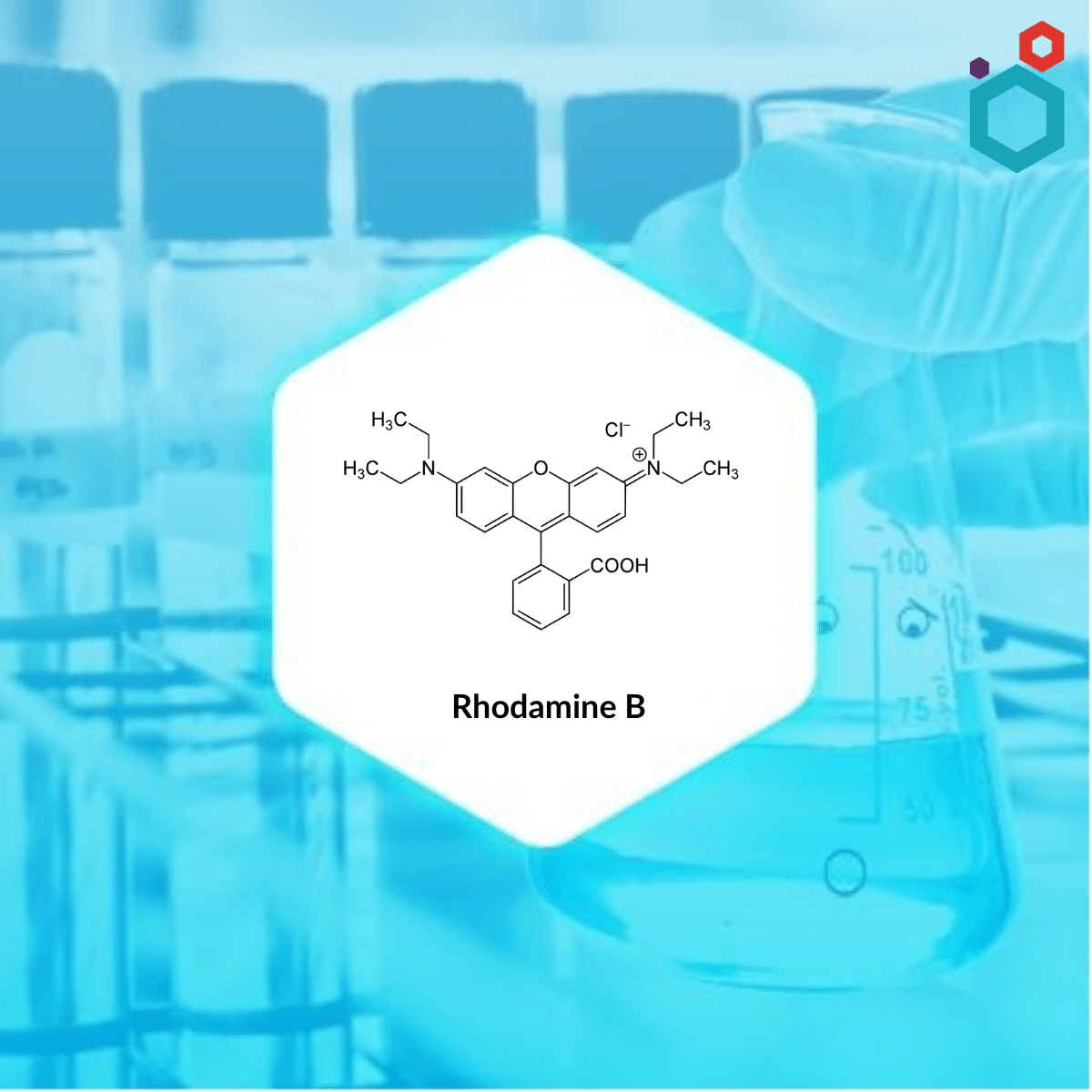
| IUPAC Name | [9-(2-carboxyphenyl)-6-(diethylamino)xanthen-3-ylidene]-diethylazanium;chloride |
| Synonyms | Basic Violet 10; Brilliant Pink B; Tetraethylrhodamine; Calcozine Red BX; Symulex Magenta F; Rhodamine 610; C.I. Pigment Violet 1; Basic Violet 10; Rodamina B |
| CAS No | 81-88-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C28H31ClN2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 479.0 g/mol |
| Color Index No | 45170 |
| Pubchem CID | 6694 |
| Pubchem SID | 475523900 |
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
| SR. No | Criteria | Limit/Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Appearance (form) | Solid Powder or Crystals |
| 2 | Appearance (colour) | Green or Reddish-Violet |
| 3 | Melting Point | 210-211°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in Water, Alcohol & Ether and Insoluble in Organic solvents |
| 5 | Solubility (Color) | Red to Very Dark Red |
| 6 | Storage | Room Temperature |
Uses
- Rhodamine B is frequently employed as a tracer dye in water to assess the rate and direction of flow and transport with the use of fluorometers since it fluoresces and is thus easily and affordably detectable.
- In biology, the fluorescent dye rhodamine B is used in combination with Auramine O as auramine-rhodamine stain to stain acid-fast organisms, e.g. Mycobacterium.
- It is also utilized to a significant extent in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA.
- Additionally, it is being investigated for potential application as a biomarker in oral rabies vaccines for wild animals like raccoons.
- The vivid shade of pink that is known as Opera Rose is achieved by combining rhodamine B and Quinacridone magenta dye.
FAQs
Q. What fluorescence is emitted by rhodamine?
Rhodamine B is a fluorescent chemical whose excitation peak occurs at 546 nm and whose emission peak occurs at 568 nm.
Q. Is Rhodamine B toxic?
It has been hypothesized that rhodamine B could cause cancer.
Resources
Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
